FASTENERS
In Petro and chemical industry for flange connections Stud Bolts and Hex Bolts are used. The Stud Bolt is athreaded rod with 2 heavy hexagon nuts, while the Hex Bolt has a head with one nut. Nuts and head are both sixsided.



Features
Bolts threading are defined in ASME B1.1 Unified Inch Screw Threads, (UN and UNR Thread Form). Thread series
cover designations of diameter/pitch combinations that are measured by the number of threads per inch (TPI) applied to a single diameter.
Standard Thre ad Pitches
- Coarse thread series (UNC/UNRC) is the most widely used thread system and applied in most of the screws, bolts and nuts. Coarse threads are used for threads in low strength materials such as iron, mild steel, softer alloy, etc. The coarse thread is also more tolerant in adverse conditions and facilitate quick assembly.
- Fine thread series (UNF/UNRF) is commonly used in precision applications and in there where require a higher tensile strength than the coarse thread series.
- 8 - Thread series (8UN) is the specified thread forming method for several ASTM standards including A193 B7, A193 B8/B8M, and A320. This series is mostly used for diameters one inch and above.

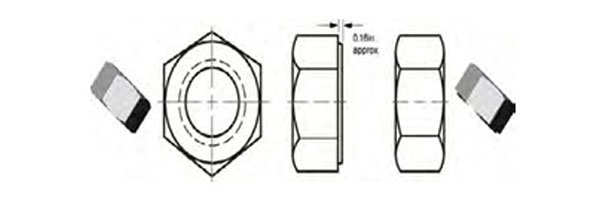
HexNuts
Hex nuts (dimensional data) are defined in ASME B18.2.2
Depending on a customer specification, nuts must be both sites chamfered or with on one side a washer-face.
Materials for Stud Bolts
Frequently used grades are A193 for thread rods and A194 for the nuts.
ASTM A193 covers alloy and stainless steel bolting material for pressure vessels, Valves, flanges, and fittings for high
temperature or high pressure service, or other special purpose applications.
ASTM A194 covers a variety of carbon, alloy, and martensitic and austenitic stainless steel nuts. These nuts are intended for high-pressure or high-temperature service, or both.
